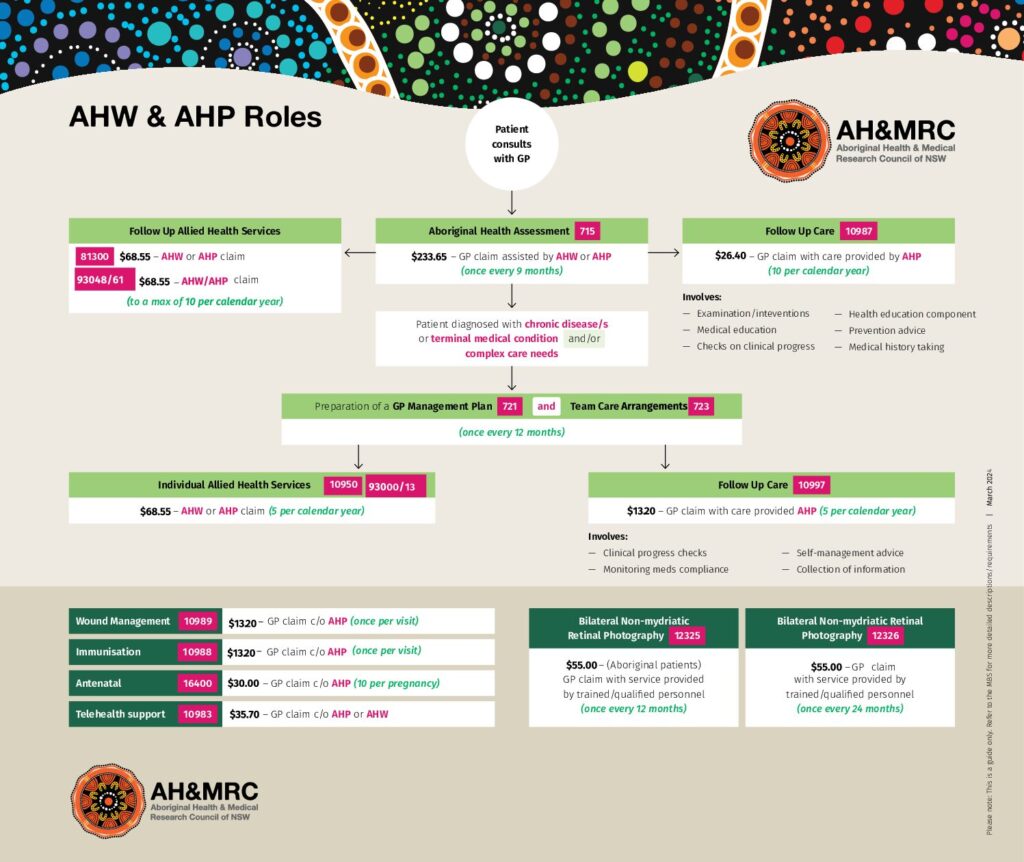
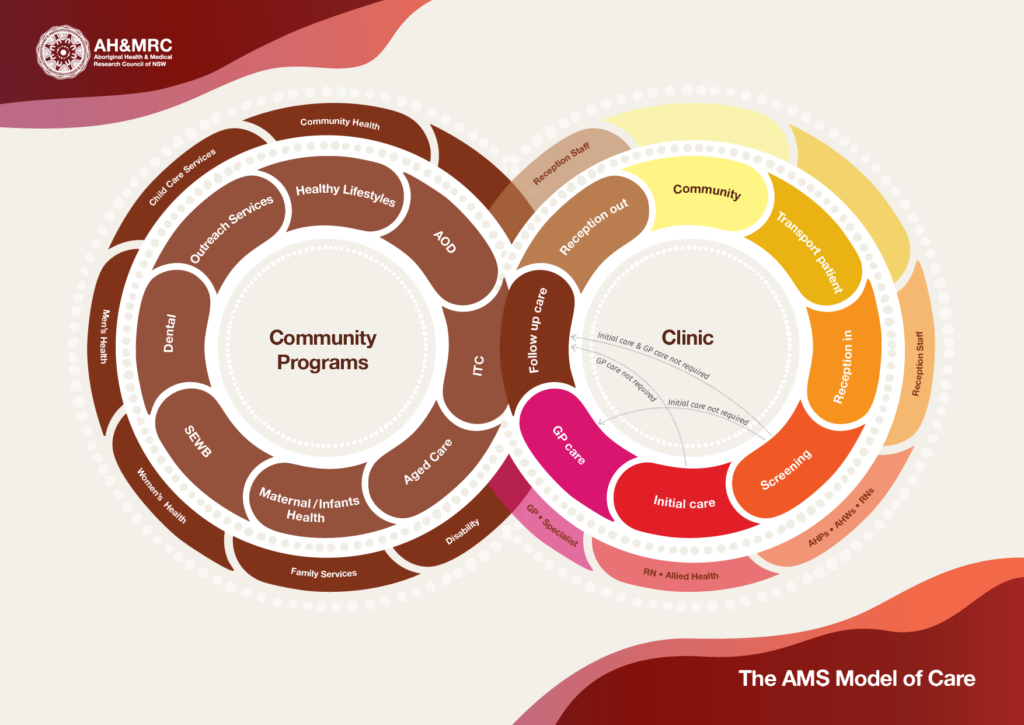
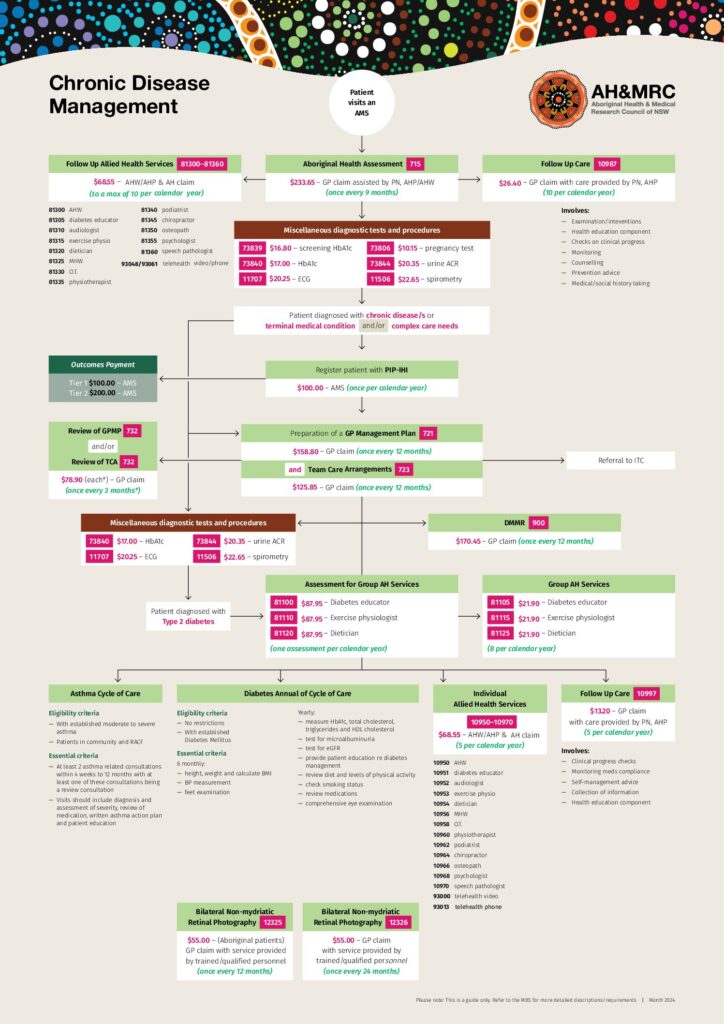
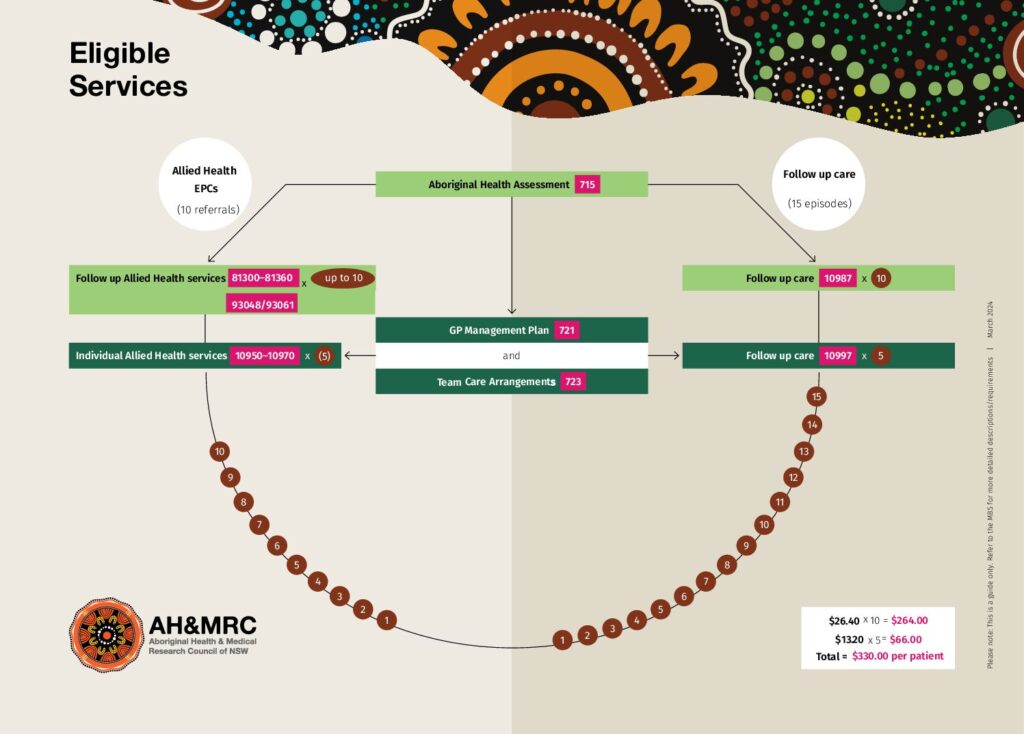
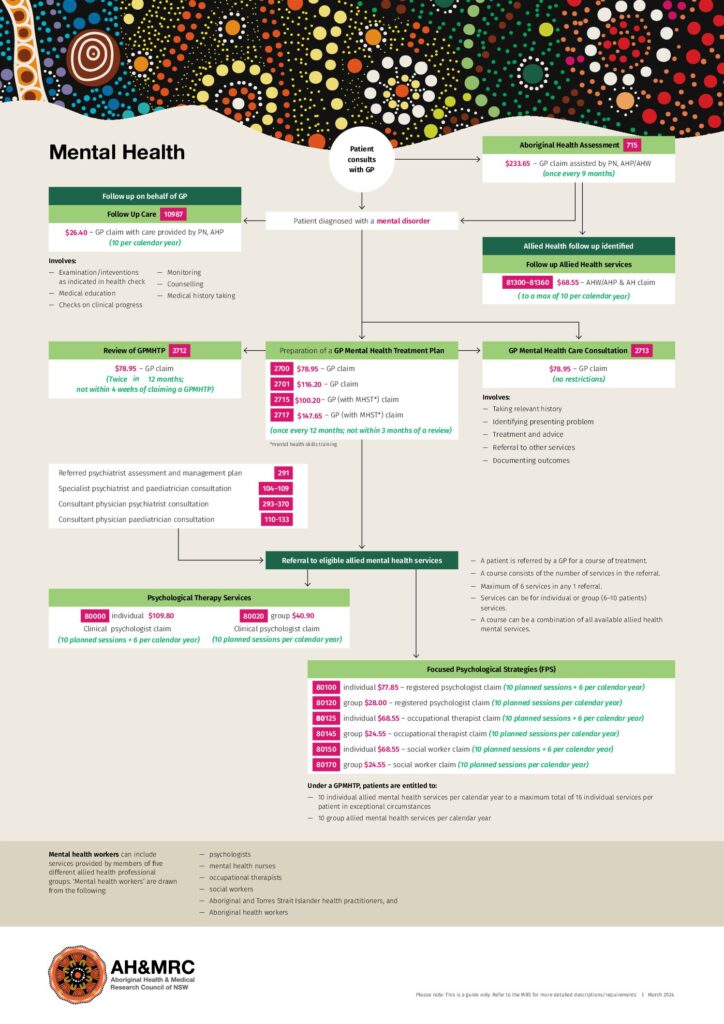
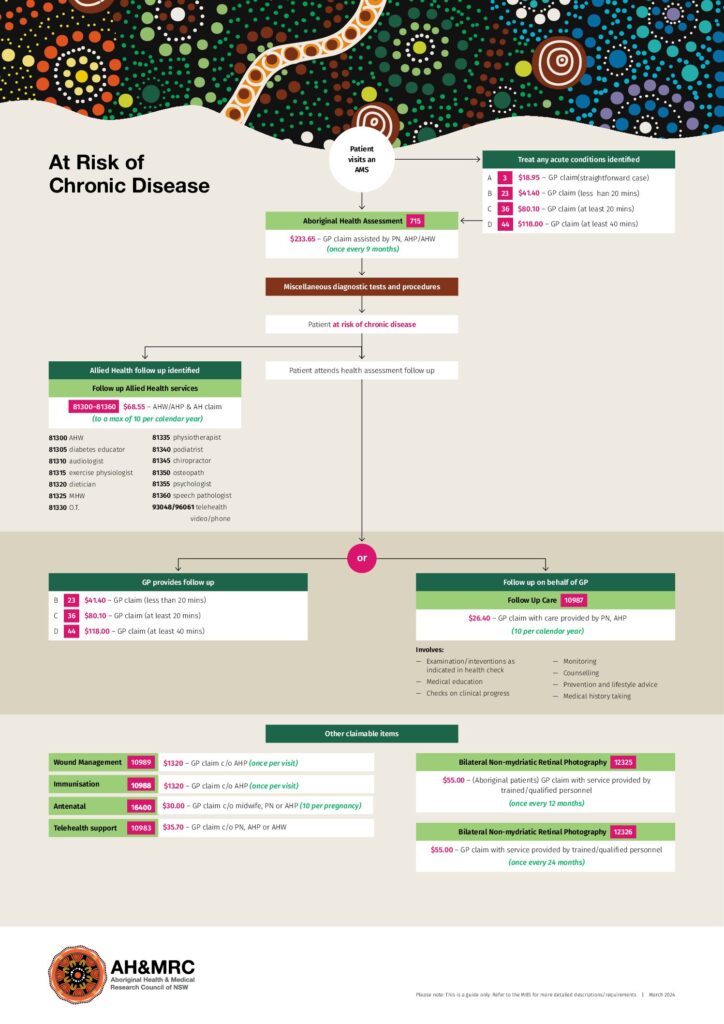
AH&MRC has been funded by the Australian Digital Health Agency to assist the ACCHS in NSW with the knowledge and resources in digital health technologies to be able to provide high-quality healthcare services to the Aboriginal communities. At AH&MRC, we believe that digital health is not merely a technology but an integral part of our organization that helps to fulfill our principle to improve the health of the Aboriginal community and help people live longer.
There are many benefits to using digital health technologies, including:
- Improved efficiency: Digital health technologies can help to improve the efficiency of healthcare by reducing paperwork, improving communication, and making it easier to access care.
- Improved quality: Digital health technologies can help to improve the quality of care by providing clinicians with more information about patients, allowing them to monitor patients remotely, and providing patients with access to educational resources.
- Increased accessibility: Digital health technologies can help to increase the accessibility of healthcare by making it easier for people to get care, regardless of their location or income.
While digital health has many potential benefits, there are also some challenges that need to be addressed, including:
- Security: Security is a major concern with digital health technologies, as patient data is often stored on these devices.
- Interoperability: Different digital health technologies often do not work together, which can make it difficult for patients to share their data with their healthcare providers.
- Digital literacy: Aboriginal people may have lower levels of digital literacy than other Australians, which can make it difficult for them to use digital health technologies.
- Cultural appropriateness: Digital health technologies need to be culturally appropriate for Aboriginal people. This means that they need to be designed in a way that is respectful of Aboriginal culture and values.
- Adoption: There is a need to increase the adoption of digital health technologies by both healthcare providers and patients.
Digital Health encompasses various aspects of digital technologies, and the National Digital Health Strategy stated seven strategic priorities that aim to transform the quality and sustainability of health and care. AH&MRC helps in the implementation of the strategy for the Aboriginal communities in NSW by emphasising the four divisions, and they are –
My Health Record, Electronic Prescription, High-quality data, and Telehealth.
My Health Record
What is My Health Record
My Health Record (MHR) is a secure online summary of your health information. It is stored in the cloud and can be accessed by you and your healthcare providers. Your record can include information such as your medical history, allergies, medications, and test results.
Benefits of My Health Record
There are many benefits to having a My Health Record, including:
- Improved communication: Your healthcare providers can access your record to see your full health history, which can help them make better decisions about your care.It allows healthcare providers from different services to access your medical information, saving time and correspondence between yourself and various medical providers.
- Reduced errors: By having access to your complete health history, your healthcare providers can avoid making mistakes, such as prescribing the wrong medication or giving you a test that you have already had.
- Increased convenience: You can use your My Health Record to view your health information anytime, anywhere. This can be helpful when you are seeing a new healthcare provider or when you are traveling.
- Better decision-making: You can use your My Health Record to track your health over time and to make informed decisions about your care.
Apart from you, the only people who can view or access your My Health Record are your healthcare providers, people you invite to help you manage your record (nominated representatives) and people who manage your record for you, if you are not able to (authorised representatives).
How to get a My Health Record
To get a My Health Record, you can create an account online or by calling the My Health Record helpline. You will need to verify your identity before you can create an account.
Once you have created an account, you can start adding information to your record. You can add information yourself, or you can ask your healthcare providers to add information for you.
You can also choose to share your record with other people, such as your family members or your carers. To share your record, you will need to give them permission.
My Health Record is a safe and secure way to store your health information. Your record is encrypted and protected by privacy laws.
If you have any questions about My Health Record, you can contact the My Health Record helpline.
Here are some additional information about My Health Record:
- My Health Record is a voluntary service. You do not have to create an account if you do not want to.
- You can close your My Health Record at any time.
- If you close your My Health Record, you will still be able to access your Medicare information.
We understand that My Health Record can be a complex system, and we are here to help you make the most of it. Our team of experts can help you connect your patient information system, find other My Health Record enabled services in your area, and train your staff on how to use My Health Record. We can also advocate on your behalf to the Australian Digital Health Agency and assist with project implementation.
We are committed to helping our members get the most out of My Health Record. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you.
For more information about My Health Record and how it can benefit you, please contact your Local Aboriginal Medical Service or speak with your GP.
For more information visit the Australian Digital Health Agency website.
Useful links for the Aboriginal Member Services
https://www.digitalhealth.gov.au/healthcare-providers/initiatives-and-programs/my-health-record
Useful links for the Consumers
https://www.digitalhealth.gov.au/initiatives-and-programs/my-health-record
Electronic Prescription
What is electronic prescription?
An electronic prescription (e-prescription) is a digital version of a paper prescription. It is a secure, electronic document that is transmitted directly from a prescriber to a pharmacy. E-prescriptions can be used to dispense medications for both acute and chronic conditions.
Benefits of electronic prescription
There are many benefits to using e-prescriptions, including:
- Improved safety: E-prescriptions help to reduce the risk of medication errors by eliminating the need for manual transcription.
- Increased convenience: E-prescriptions make it easier for patients to get their medications. Patients can take their e-prescription to any participating pharmacy, and they do not need to worry about losing or misplacing a paper prescription.
- Better communication: E-prescriptions improve communication between prescribers, pharmacists, and patients. This can help to ensure that patients are taking the correct medications and dosages, and that they are aware of any potential side effects or interactions.
How to get an e-prescription
To get an e-prescription, simply ask your prescriber if they offer e-prescriptions. If they do, they will be able to create an electronic prescription for you during your consultation. You will then receive a unique barcode (known as a “token”) via SMS or email. Take this token to any participating pharmacy to have your medication dispensed.
What if my pharmacy does not accept e-prescriptions?
If your pharmacy does not accept e-prescriptions, you will still be able to get a paper prescription from your prescriber. However, e-prescriptions are becoming increasingly common, so it is worth checking with your pharmacy to see if they plan to start accepting them in the future.
Conclusion
E-prescriptions are a safe, convenient, and effective way to manage medications. If your prescriber offers e-prescriptions, AH&MRC encourages you to ask for one. It is a small step that can make a big difference in the safety and quality of your care.
To learn more about the electronic prescription:
Electronic prescriptions for prescribers (digitalhealth.gov.au)
Factsheets
How electronic prescriptions work: for prescribers https://www.digitalhealth.gov.au/sites/default/files/2020-11/Electronic_prescriptions-An_overview_for_prescribers.pdf
How electronic prescriptions work: for dispensers https://www.digitalhealth.gov.au/sites/default/files/2020-11/Electronic_prescriptions-An_overview_for_dispensers.pdf
Secure Messaging
What is secure messaging?
Secure messaging is a way to send and receive messages that are protected from unauthorized access. This is done by using encryption, which scrambles the message so that it can only be read by the intended recipient. Secure messaging is often used in healthcare, financial services, and other industries where sensitive information is exchanged.
Benefits of secure messaging
There are many benefits to using secure messaging, including:
- Security: Secure messaging helps to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Compliance: Secure messaging can help organizations to comply with industry regulations, such as HIPAA and GLBA.
- Efficiency: Secure messaging can help to improve efficiency by reducing the need to print, scan, and fax documents.
- Cost savings: Secure messaging can help to save organizations money by reducing the cost of postage, printing, and scanning.
How does secure messaging work?
Secure messaging uses encryption to protect messages from unauthorized access. When a message is sent, it is encrypted by the sender’s computer. The encrypted message is then sent to the recipient’s computer, where it is decrypted and read.
There are two main types of encryption used in secure messaging:
- End-to-end encryption: This type of encryption encrypts the message from the sender’s computer to the recipient’s computer. No one in between, not even the service provider, can read the message.
- Transport layer security (TLS): This type of encryption encrypts the message while it is in transit between the sender’s and recipient’s computers. The service provider can decrypt the message, but only to deliver it to the intended recipient.
How to choose a secure messaging solution
When choosing a secure messaging solution, there are a few factors to consider, including:
- Security: The solution should use strong encryption and should be certified by a reputable security organization.
- Compliance: The solution should be compliant with industry regulations, such as HIPAA and GLBA.
- Features: The solution should have the features that you need, such as the ability to send and receive messages, create groups, and store messages.
- Cost: The solution should be affordable for your organization.
Data Quality
Data quality in clinical records refers to the accuracy, completeness, and timeliness of the information contained in a patient’s medical record. High-quality patient clinical data is essential for improving patient care. By collecting and using this data, healthcare providers can better understand the needs of their patients, identify patients who are at risk for certain diseases or conditions, and develop and test new treatments. High-quality patient clinical data can also be used to improve the quality of care provided to patients, make informed decisions about healthcare policy, and ultimately improve the health of the population.
There are a number of things that can be done to improve data quality, including standardization, education, technology, and auditing. By taking these steps, healthcare organizations can improve the quality of care for their patients and reduce the risk of errors.
Visit ADHA website https://www.digitalhealth.gov.au/healthcare-providers/initiatives-and-programs/interoperability-and-data-quality to learn more about data quality.
AH&MRC offer online and in-person training for members who need help with data quality. To schedule a training session for your team, please contact our Digital Health team.
Telehealth
Telehealth refers to video and telephone calls to conduct health consultations, which are available for a range of health services by General Practitioners (GPs), Nurse Practitioners, Aboriginal Health Practitioners and Workers, Mental Health professionals, Allied Health professionals and some medical specialists. Telehealth is a significant strategy that ensures people can continue to access essential health services while reducing the risk of exposure to COVID-19. It can be used for consultations, intervention, prescriptions, referrals, education, and or supervision.
Call your AMS first and discuss whether you could have a Telehealth consultation or need to come to the clinic in person instead.
For more information read our Telehealth Factsheet for community members.
https://www.ahmrc.org.au/the-triumph-of-telehealth/
Training and Support
The Australian Digital Health Agency (ADHA) offers webinars for health practitioners, clinicians, and health workers. These webinars provide an opportunity to learn about digital health and how to integrate it into your practice.
The ADHA webinars cover a wide range of topics, including:
- My Health Record
- Electronic prescribing
- Telehealth
- Secure messaging
- Clinical decision support tools
- Data analytics
- And more!
The ADHA webinars are free to attend and are available to anyone who works in the health care sector. To register for a webinar, visit the ADHA website.
By attending an ADHA webinar, you can learn about the latest digital health trends and how to use them to improve the care you provide to your patients.
Here are some additional details that you may want to include in your rewrite:
- The ADHA webinars are held on a regular basis. You can find a schedule of upcoming webinars on the ADHA website.
- The ADHA webinars are led by experts in the field of digital health. This ensures that you will receive accurate and up-to-date information.
- The ADHA webinars are interactive. This means that you will have the opportunity to ask questions and get feedback from the experts.
Webinars for healthcare providers https://www.digitalhealth.gov.au/healthcare-providers/webinars
Information about my health App https://www.digitalhealth.gov.au/myhealth